Unveiling the Shopping Secrets: The Psychology of Casual Buying
Have you ever found yourself wandering aimlessly through a store, only to walk out with a bag full of items you never intended to buy? This phenomenon is known as casual buying, and it is a fascinating area of study in the field of consumer psychology. In this article, we will delve into the science behind casual buying and explore the psychology behind our purchase decisions.
At its core, casual buying is driven by a complex interplay of psychological factors that influence our shopping behavior. One of the key drivers of casual buying is the concept of impulse buying. When we see an item that captures our attention, our brains release dopamine, the feel-good hormone, which gives us a sense of pleasure and satisfaction. This rush of dopamine can lead us to make impulsive decisions and purchase items on a whim.
Another factor that plays a significant role in casual buying is the power of suggestion. Retailers are skilled at using subtle cues, such as product placement and promotional offers, to influence our purchase decisions. For example, placing items at eye level or offering limited-time discounts can create a sense of urgency and compel us to make a purchase without much thought.
In addition to impulse buying and the power of suggestion, our emotions also play a crucial role in casual buying. Research has shown that our emotions can heavily influence our shopping behavior, with feelings of happiness, excitement, or even boredom driving us to make impulsive purchases. For example, if we are feeling stressed or anxious, we may be more likely to engage in retail therapy and buy items to boost our mood.
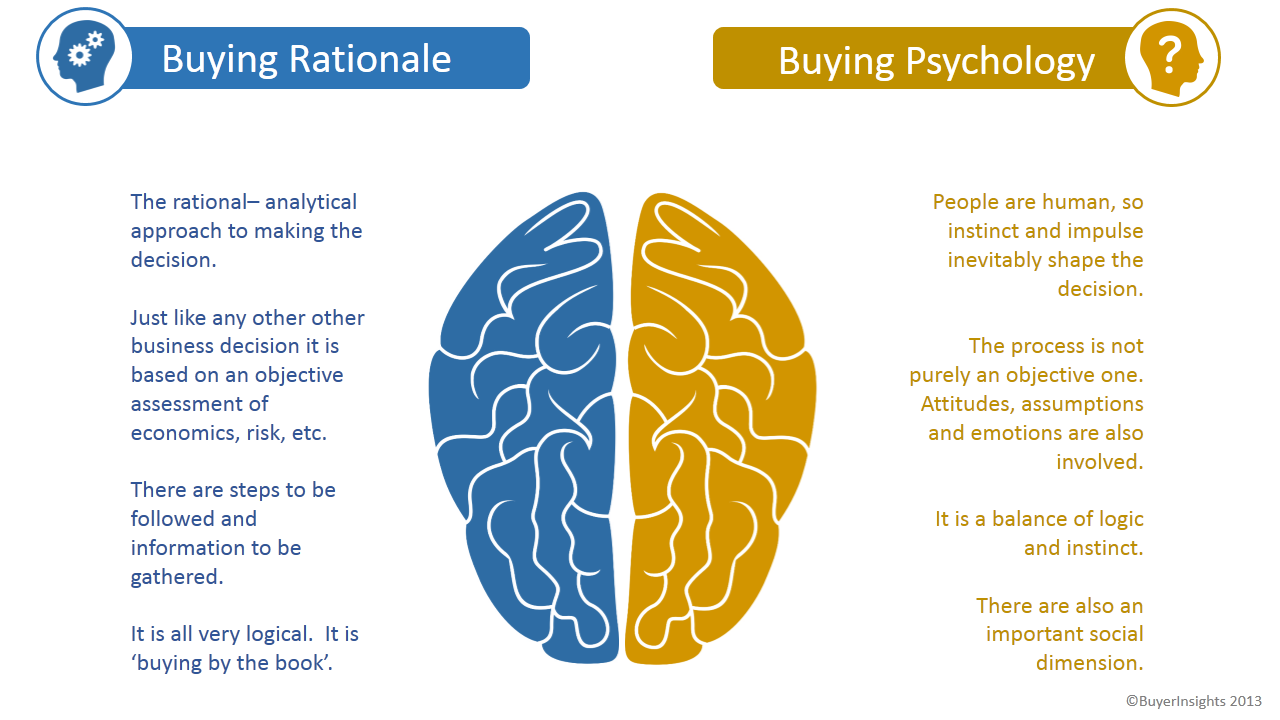
Image Source: sellerinsights.com
Furthermore, our social environment can also impact our casual buying habits. Peer pressure, social norms, and the desire to fit in with others can all influence our purchase decisions. For example, if we see our friends or influencers on social media buying certain products, we may feel compelled to follow suit and make similar purchases to feel included.
The concept of scarcity and exclusivity is another powerful driver of casual buying. Humans are naturally drawn to items that are perceived as rare or limited edition, as they hold a higher value in our minds. Retailers often use tactics such as limited-time offers or exclusive product releases to create a sense of scarcity and drive up demand for their products.
Finally, the element of convenience also plays a significant role in casual buying. With the rise of online shopping and one-click purchasing, it has become easier than ever to make impulsive purchases with just a few taps on our smartphones. The convenience factor can lead us to make quick and thoughtless decisions, adding to the allure of casual buying.
In conclusion, casual buying is a fascinating area of study that sheds light on the complex psychology behind our purchase decisions. From impulse buying to the power of suggestion, emotions, social influences, scarcity, and convenience, a multitude of factors come into play when we engage in casual shopping. By understanding these psychological drivers, we can gain insight into our own shopping behavior and make more informed decisions when it comes to casual buying. So next time you find yourself tempted to make an impulsive purchase, remember the science behind casual buying and think twice before adding that item to your cart.
From Window Shopping to Splurging: Understanding Purchase Choices
Have you ever found yourself wandering through a shopping mall, casually browsing through the latest trends and newest gadgets, only to walk out with bags full of items you never intended to buy? This phenomenon, known as casual buying, is a common occurrence that many people experience. But what exactly drives these impulsive purchase decisions?
The psychology behind purchase choices is a fascinating subject that delves deep into the inner workings of the human mind. From the moment we lay eyes on a product to the moment we decide to make a purchase, our brains are constantly processing information and making split-second decisions. Understanding the factors that influence these decisions can shed light on why we buy certain things and how marketers can capitalize on these tendencies.
One of the main drivers of casual buying is the concept of emotional impulse. When we see something that catches our eye, whether it’s a shiny new gadget or a stylish piece of clothing, our emotions kick in and override our rational thoughts. This emotional response can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as the color, design, or brand of the product. Marketers are well aware of this phenomenon and often use it to their advantage by creating visually appealing advertisements and displays that are designed to evoke a strong emotional response.
Another factor that plays a significant role in purchase decisions is social influence. We are social creatures by nature, and we often look to others for validation and approval. When we see our friends or favorite celebrities using a certain product, we are more likely to want to own it ourselves. This desire to fit in and be part of the crowd can drive us to make impulse purchases, even if we don’t necessarily need or want the item in question.
In addition to emotional impulse and social influence, another important factor that affects purchase choices is cognitive bias. Our brains are wired to take shortcuts and make quick decisions based on limited information. This means that we often rely on heuristics, or mental shortcuts, to make decisions without fully considering all the available options. For example, we may be more likely to purchase a product if it is labeled as a limited-time offer or if it is displayed prominently in a store window. These subtle cues can nudge us towards making a purchase without us even realizing it.
Furthermore, the concept of scarcity plays a significant role in driving purchase decisions. When we perceive a product to be in limited supply or high demand, we are more likely to place a higher value on it and feel a sense of urgency to buy it before it runs out. This fear of missing out, or FOMO, can push us to make impulsive purchases in order to secure the item before it’s too late. Marketers often use tactics such as limited edition releases and flash sales to capitalize on this sense of urgency and drive sales.
In conclusion, casual buying is a complex phenomenon that involves a multitude of psychological factors. From emotional impulse and social influence to cognitive bias and scarcity, our purchase decisions are influenced by a variety of subconscious cues and triggers. By understanding the science behind these tendencies, marketers can better tailor their strategies to appeal to consumers’ emotions and drive sales. So the next time you find yourself window shopping and end up splurging on something unexpected, remember that there is a science behind your purchase choices.
Understanding the Psychology of Buying Decisions